 TheStaticTurtle
TheStaticTurtleUsing the Raspberry Pi Pico and circuit python with a joystick to control the computer mouse
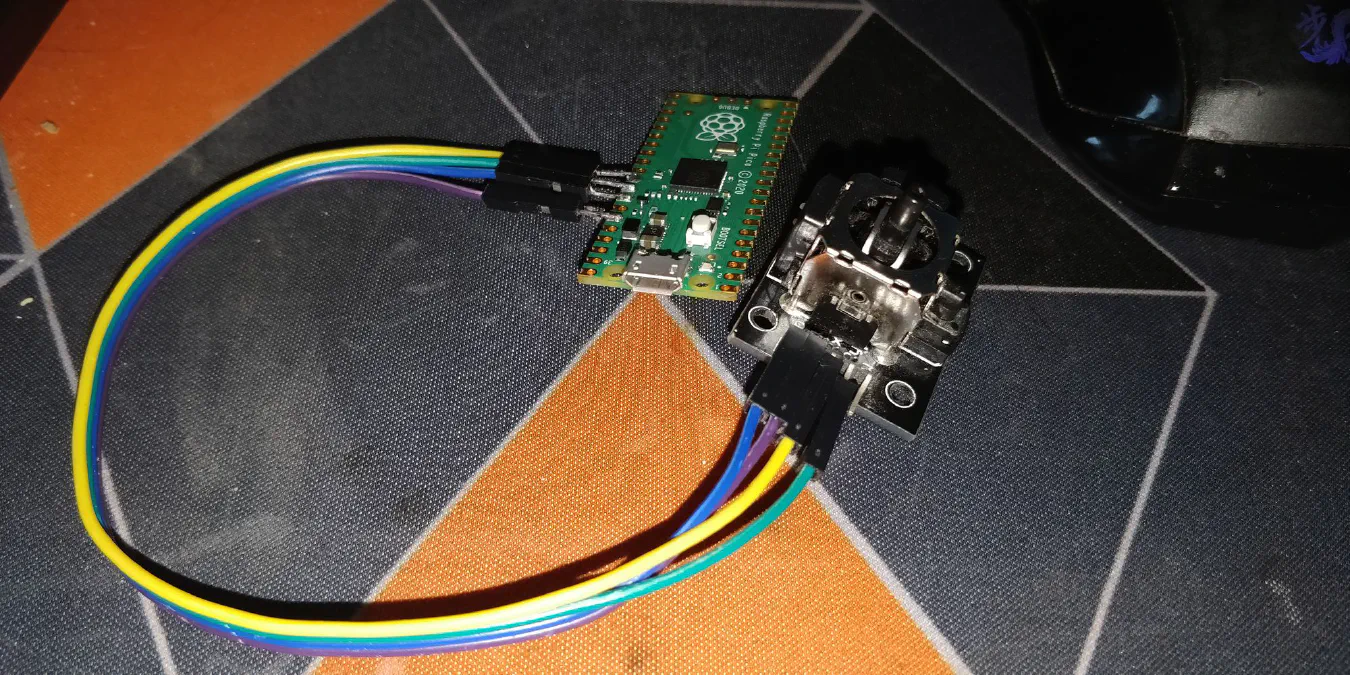

A few days ago I bought a Raspberry Pi Pico the first thing I did was to flash micropython on it.
The process was quite simple, press the button, plug it in and transfer the file. After playing a bit with the REPL interpreter I was left with two Picos and no project idea.
So I searched a bit on the internet and I found that the RP2040 supports HID, so I started to look in that direction. As far as I looked the micropython firmware provided by the Raspberry Pi foundation did provide hid support, So I look for alternative.
Fortunately, Adafruit Circuit Python is compatible with the Pi Pico and that one supported hid as some other thing (like showing up as a drive to transfer code). So I did the updating procedure again but with this firmware.
I then got the adafruit_hid folder from this GitHub repo
and dragged it onto the pico storage. I then started a terminal and jumped into the REPL interpreter a few lines of code later. A few lines of code later I was ready to go:
import usb_hid
from adafruit_hid.mouse import Mouse
mouse = Mouse(usb_hid.devices)
mouse.move(10,0)
I then proceeded to solder a joystick to it following this very simple schematic: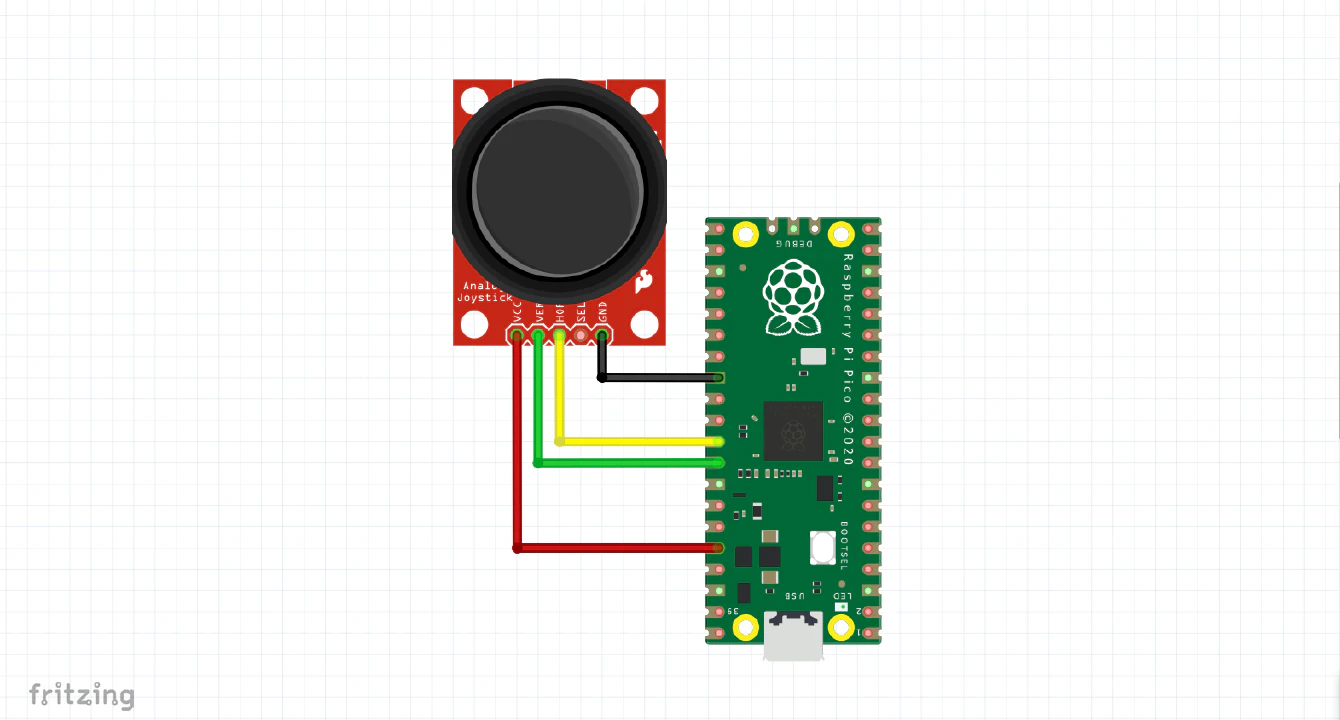
import board
from analogio import AnalogIn
import usb_hid
from adafruit_hid.mouse import Mouse
mouse = Mouse(usb_hid.devices)
xAxis = AnalogIn(board.A1)
yAxis = AnalogIn(board.A0)
in_min,in_max,out_min,out_max = (0, 65000, -5, 5)
filter_joystick_deadzone = lambda x: int((x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min) if abs(x - 32768) > 500 else 0
while True:
x_offset = filter_joystick_deadzone(xAxis.value) * -1 #Invert axis
y_offset = filter_joystick_deadzone(yAxis.value)
mouse.move(x_offset, y_offset, 0)
The first 5 lines are for importing the necessary modules to read the analog signals and control the mouse.
The next 3 lines are declaring the objects representing the mouse and the two analog pins
Next is a lambda function, in short this creates a function named filter_joystick_deadzone which will return 0 if the joystick is in +/- 500 of the center value (32768) or else it will convert the value to a range of -5 to 5
Next is a while loop that reads the inputs, pass them to the filter and move the mouse
Here is a quick demo video:
Want to chat about this article? Just post a message down here. Chat is powered by giscus and all discussions can be found here: TheStaticTurtle/blog-comments